With radiology now fully digital, efficiently manipulating DICOM medical images requires robust viewing software offering vast functionality from multiplanar reconstructions to volume rendering.
Unfortunately, packed-to-the-brim commercial platforms carry exorbitant licensing fees, sending frugal folks on a hunt for DICOM software free alternatives.
This article outlines the feature limitations of gratis DICOM viewers and discusses future prospects for affordable self-hosted apps matching all capabilities required by radiology learners and niche specialists alike.
The Growing Complexities of Modern Medical Imaging
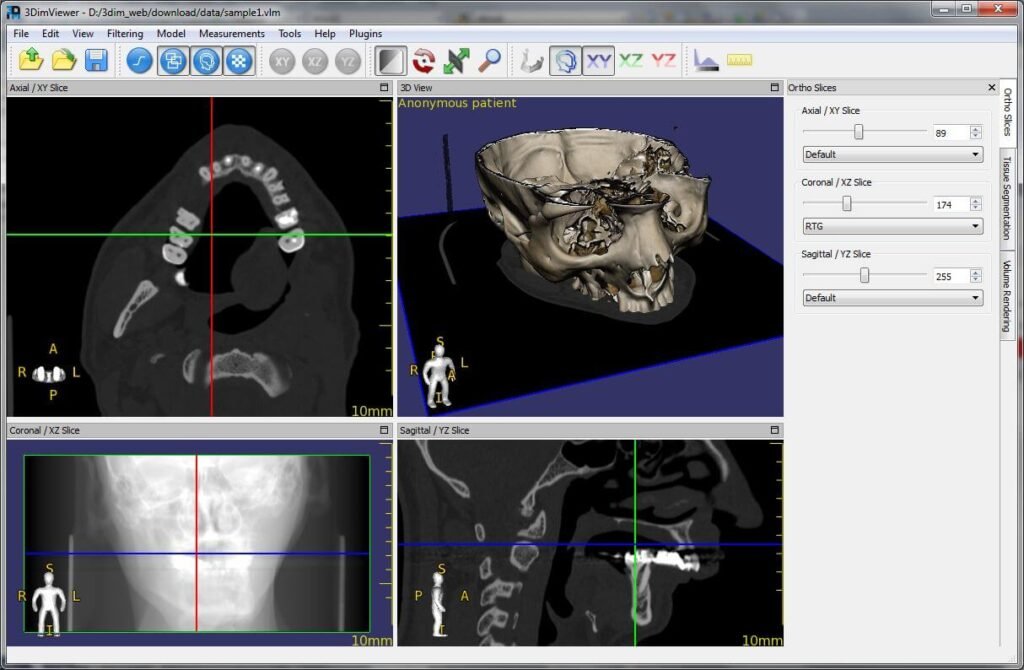
Legacy X-rays providing singular planar perspective now seem quaint compared to quantitative multidimensional modalities like CT and MRI generating expansive datasets from voxels.
Such volumetric information allows unprecedented anatomical manipulation through:
- Multiplanar reformations: Dynamically browsing arbitrary imaging planes
- 3D modeling: Surface and volume rendering anatomy in diverse styles
- Quantitative analytics: Precise biometrics of tissue and tumor properties
Unfortunately, efficiently leveraging these powers demands equally advanced DICOM viewers with immersive toolsets beyond basic display.
Current Limitations of Free DICOM Viewers
Presently, gratis DICOM apps like OrthancViewer shine at economical archival tasks but falter attempting heavier diagnostic lifting due to a lack of:
- Streamlined multiplanar reconstructions
- Intuitive cine loop controls
- Diverse 3D volume rendering options
- Integrated quantitative analytics
- Customizable automated image presets
While adequate for reference, such constraints make free DICOM viewers ill-suited as sole solutions for routine use.
The Challenges Constraining Open Source Innovation
Despite vibrant developer communities surrounding platforms like Orthanc, several factors curb faster matching of proprietary functionality, including:
- Project reliance on volunteer efforts
- Absence of guided financial incentive mechanisms
- Developer inexperience with complex medical viewers
- Limited publicly available interface usability testing
Thus, progress often meanders incrementally based on sporadic community contributions.
The Promise of Integrated Development Frameworks
Despite current limitations in free DICOM viewers, the long-term solution may involve integrated platforms streamlining open medical image computing like MITK, 3D Slicer, or Syngo Via, offering:
- Modular, extensible architecture readily tailored to needs
- Unified documentation easing onboarding
- Curated UX/UI design language accelerating iteration
As integrated solutions gain traction, facilitating decentralized collaborator contributions across domains, they could catalyze free DICOM viewer maturation, closing the feature gap.
Commercial SaaS Offers a Middle Path
Rather than waiting for fully self-hosted gratis viewers to reach feature parity, low-cost SaaS DICOM viewers like Annotos provide a middle path today with intuitive tools at accessible pricing, though without source control.
SaaS alleviates infrastructure burdens targeting core usage needs at economical rates for learners and smaller practices through scalable cloud delivery.
While gratis DICOM lags proprietary viewers, community-driven collaboration hopes to accelerate enhancement if compelling frameworks gain adoption. Until then, affordable SaaS subscriptions bridge the gap.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can free viewers render 3D visualizations?
Most free viewers have limited 3D rendering capabilities. Basic surface reconstructions may display, but advanced volumetric views and quantitative analyses are often unavailable.
Do free DICOM viewers work on all operating systems?
Popular free options like Orthanc provide cross-platform support across Windows, MacOS, and Linux. Some niche-free viewers only work on Windows currently. Web-based HTML5 viewers are OS-agnostic.
What modalities can free viewers analyze?
Most free DICOM software reads basic modalities like CT, MRI, PET, and ultrasound. Support for specialized formats like ophthalmology, endoscopy video, and quantitative parametric maps needs testing for each viewer.
Can I use a free viewer if my studies have thousands of images?
Loading studies with very large volumes of images and series strains free DICOM software. Such dense examinations often require commercial platforms or custom databases for fluid navigation.